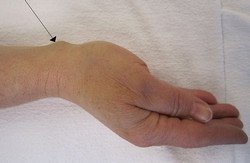
What is a Ganglion Cyst?
Ganglion cysts are small nodules that usually appear near the muscles, tendons, and bones of the feet or hands. This type of growth or cyst is also referred to as the “Bible cyst” or “Bible bump” because of a common misconception about the condition in the earlier days of medicine wherein the ganglion cyst is eradicated by smashing it with a hard object, usually a heavy and hardbound book like the Bible, it was not until much later that this practice was discontinued because it was found out that causing the cyst to rupture does not help the condition at all and oftentimes, can make it worse. The size and extent of the ganglion cyst can change as weeks and months pass; it can either shrink or enlarge depending on the conditions.
Ganglion Cyst Symptoms
The first signs and symptoms of ganglion cysts are usually the small swollen or elevated portion of the skin usually mistaken for a small insect bite but without the itch and skin irritation. The swelling can either appear suddenly or slowly emerge over a period of time, it can even disappear completely only to show itself on the same site or move a few inches from the original site after an indefinite period of time. The cyst can change its size from time to time without any relation to outside forces, the bump is generally described as ranging between 0.4 to 1.2 inches or 1-3 centimeters, and non mobile, or does not move when palpated.
Although not all, a good amount of people with ganglion cysts, around 70 percent, often experience acute pain from the condition, this is more common when the bump has experienced trauma since the raised portion is more likely to be bumped against a hard surface or brush against a rough surface when doing daily activities. In the situation where the ganglion cyst is directly on a tendon or a joint, the muscles surrounding the area may experience some sort of weakness and numbness. The pain characteristics are described as dull, throbbing, cannot be relieved by a change in position, and the severity can be increased by motion.
Ganglion Cyst Causes
Ganglions cysts may contain a clear and viscous fluid like that of interstitial fluids, it is an idiopathic condition, meaning the causes are vague and largely unknown, but certain studies point to an abnormality in the member that covers muscles and tendons. A popular notion is that these membranes accidentally for a kind of sack where fluids can gather but cannot get back out; another theory is that these cysts can be caused by repeated trauma to the area since a good number of athletes who experience frequent stress on joints like their wrists. Men are also less prone to the condition that women, so there might be a relation to the varying hormones of men and women
Ganglion cyst in wrist
A ganglion cyst located in the immediate area of the wrist is the most common type of ganglion cyst, with occurrences accounting for up to 80 percent of the total ganglion cyst incidences, they are commonly found in the scapho-lunate joint of the wrist. These types of ganglion cysts are generally regarded as harmless unless it causes pain to the person who has it, they are usually self limiting and can disappear over time even without intervention.
Ganglion cyst in finger and thumb
Ganglion cysts that are located near the thumb and other fingers of the hand may cause some degree of discomfort especially if they appeared on the dominant hand, they are also called mucous cysts of the phalanges.
Ganglion cyst in knee
Because the knee is one of the most abused joints of the body, it is also a common site for the appearance of ganglion cysts. Repeated injuries like sprains and strains may injure the delicate membranes covering the knee. Cysts forming on the back of the knee are also called popliteal ganglion cysts or baker cysts.
Ganglion cyst on foot
Ganglion cysts that appear on the dorsal or ventral area (top or bottom) of the foot is also related to repeated trauma, either by recent injuries or the constant rubbing of things like footwear on the area, irritating the skin and the underlying tissues.
Ganglion Cyst Pictures
Picture 1 : Ganglion cyst on hand
Image source : ganglioncystinwrist.org
Picture 2 : Ganglion cyst on hand
Image source : WIKIPEDIA.ORG
Image source : wikipedia.org
 Picture 4 : Ganglion cyst on foot
Picture 4 : Ganglion cyst on foot
Photo source : helpfulhealthtips.org
Ganglion Cyst Treatment
Because most ganglion cysts are considered harmless, the first line of treatment has nothing to do with surgery, small and non painful cysts are just observed until they take care of themselves, another measure is to prevent further irritation to the site by immobilizing or placing a brace or splint on the affected joint to prevent it from moving, further measures are employed depending on the progress of the condition from there. Another common treatment is the sucking out of the fluid from the sack using needles attached to syringes, in a process called aspiration. The risk to these non surgical treatments is that a substantial amount of the cyst is still present in the area, which might cause it to reappear over time.
Ganglion Cyst Surgery (Excision and Removal)
Ganglion cyst excision is the most common surgical method of ganglion cyst removal and by far, the most effective means of permanently removing the ganglion cysts. The surgery is a fairly simple process and can be done on a outpatient basis, meaning the patient does not need to stay at the hospital overnight for surgical preparation, the patient may also go straight home after the ganglion cyst removal by surgery and continue his or her recovery at home. Smaller cysts on the phalanges can be removed after using local anesthesia, but the larger ones on areas like the wrists, knees, and ankles will more often than not require a stronger anesthesia like a general or regional anesthetic. The surgery itself is done by making a small incision over the site of the cyst, once the cyst is visualized, it is carefully isolated from the rest of the tissues and look for its source, once this is done, careful cutting away of the tissue is done to remove as much of the cyst as possible.