What are sunspots on skin
These are dark portions or spots of the skin. They are also called solar lentigines (1, 2).
They develop more often after exposure to direct sunlight (2). Sunlight has ultra violet rays (UV rays) which are responsible for the development of these spots hence the name solar Lentigines (1). Exposure to the sun darkens and increases the number of the spots (2)
What causes the Sunspots on Skin?
The sunspots on the skin are more frequently caused by prolonged exposure to UV light from the sun (1). They are also caused by exposure of UV lights from tanning beds (2).
When the skin is exposed to the UV rays, special cells of the skin called melanocytes produce increased amounts of a substance called melanin in that region (2). Melanin pigment usually protects the skin against the effects of the UV rays (3). Every time the skin is exposed to the sun (UV rays) melanin is synthesized and the skin appears darker (3, 4).
Some authors also refer to them as
- Freckles (5),
- Senile freckles or old age spots (6)
- Liver spots (7).
They were called liver spots because initially, they were thought to all be caused by liver problems (8)
In an individual with sunspots on the skin, there is accumulation of melanin within the skin cells (keratinocytes) due to increased synthesis by the melanocytes (6).
Note that the number of melanocytes varies as distinguished by Hunter, Savin and Dahl (9), even if other authors have used the names interchangeably. The author notes that in contrast to freckles, lentigines have increased number of melanocytes.
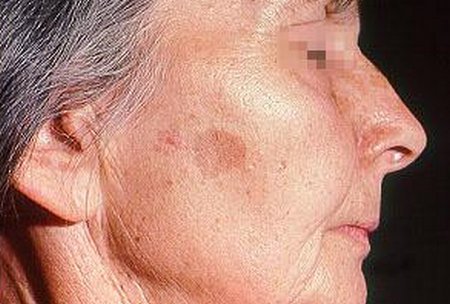
Image 1: Sunspot on the side of the face
Picture Source: emedicine.medscape.com
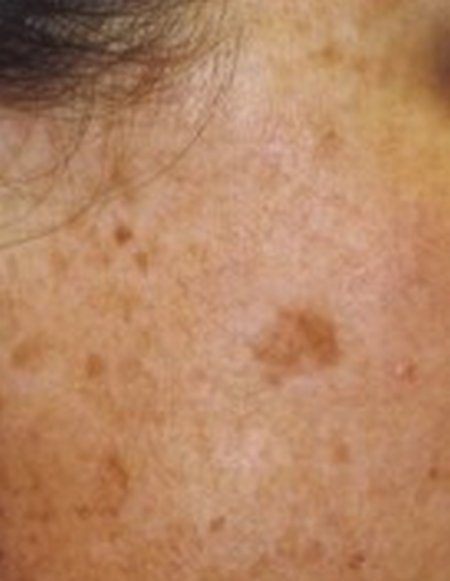
Picture 2: Sunspots on the side of the face
Photo Source: www.drbaileyskincare.com
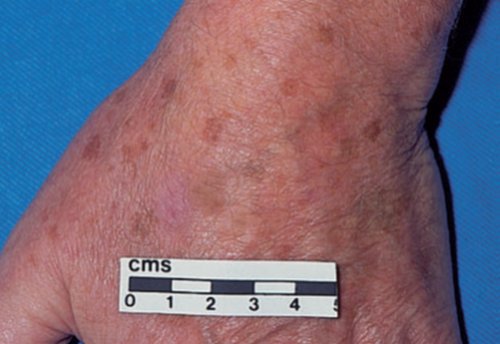
Image 3: Sunspots on the back of hand
Picture Source : Hunter, Savin and Dahl. Clinical Dermatology 3rd Edition. Massachusetts: Blackwell Science LTD 2002
Who can develop the Sunspots?
People of all ages are susceptible if they get exposed to UV rays without proper protection. However;
- Those with lighter skin develop sun spots more frequently than those with darker skin (1, 7). This is because darker persons have better natural pigment protection of melanin as compared to light skinned persons (7, 10). This makes them more resistant to sun’s harmful effects(10)
- Albinos have no melanin in their skin and therefore there are more at risk of developing sun spots and more vulnerable to the damaging effects of the UV rays
- Older persons above 40 years will commonly have the senile freckles (6)
Where do you commonly develop Sunspots?
The Lentigos are usually brown to dark colored spots on the skin. Usually they will appear on the areas of great exposure to the UV rays. These areas include (2)
- Top of the scalp
- Sides of the face
- Sides of the neck
- Back of the hands
- Other areas exposed e.g back of the body if someone was sun bathing
How to get rid of Sunspots on skin ?
Sunspots are not dangerous but they cause discomfort since they are unsightly. However, it would be important to see a dermatologist to be sure that the dark /brown spots are actually sunspots because the spots of a melanoma (skin cancer) appears the same (2). Sunspots have been said to obscure the diagnosis of a melanoma. To distinguish the two, the doctor will perform a biopsy.
The sunspots spots can be eliminated via several methods (1). The following are suggested;
- Application of creams, lotions and other cosmetic products to remove the spots
- Eating certain foods to boost their levels in the body
- Medical treatments
The products that can be applied on the skin and have been shown to fade the spots are;
- Sun block creams – one should use a sunblock every time they anticipate exposure to the sun. It is recommended that sun screens should be worn everyday over exposed skin (4). It not only promotes healing of the skin but also protects against future formation of these spots. A minimum of SPF 15 must be used for optimal effectiveness(1)
- Do IT yourself remedies – these are remedies that one does not have to purchase. They can easily be made in the comfort of the home. They are natural products that are also easily available. These include
a. Aloe Vera gel applied twice a day
b. Lemon juice
c. Fresh tomato
d. Apple cider vinegar and onion juice – mix equal parts of onion juice with apple cider vinegar. Apply the mixture on the skin for 10-5 minutes. Wash off with water
e. Garlic juice which can either be applied on the areas of the skin with the spots or can be drunk
f. Mixture of cod liver oils and castor oil in equal parts. Apply to the skin twice a day - To prevent sun spots it is important to avoid UV rays exposure by (4, 10)
a. Applying sunscreen at all times over areas exposed to the rays
b. Wearing hats
c. Seeking shade whenever possible to avoid direct sunlight if possible
What to include in diet to reduce Sunspots
Eating the following foods provide nutrients that help to reduce and eliminate sunspots;
- Fruits and vegetables – Citrus fruits contain vitamin C that the body requires to repair worn out tissues. Eat plenty of oranges, tangerine and passion fruits. Watermelons, grapes and tomatoes contain a product called lycopene which help the body avoid sunburns. Green vegetables provide vitamins B and E essential for skin health (1)
- Green tea- green tea provides antioxidants (1)
- Fish
Medical and Surgical Treatments
Even though active treatment is not needed, topical creams may be prescribed to clear the spots on the skin. These may include skin lightening creams for example hydroquinone which suppresses melanocyte metabolic processes (7) and use of retinoid cream.
In surgical treatments, freezing with liquid nitrogen in cryotherapy has also been found to be effective for solitary spots (7). Chemical peels and Laser treatment may also be done.
References :
- MDHealth.com. Sunspot on skin http://www.md-health.com/Sunspots-On-Skin.html
- http://www.drbaileyskincare.com/blog/sunspots-on-skin/
- Waugh A and Grant A. Ross and Wilson anatomy and Physiology in health and Illness. 10th edition. Edinburgh: Elsevier; 2006
- http://www.drbaileyskincare.com/blog/skin-sun-spots/
- Freckle. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Freckle
- DermNet NZ. solar Lentigo http://www.dermnetnz.org/lesions/solar-lentigo.html
- Schwartz, R. A Lentigo. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1068503
- Liver spot. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liver_spot
- Hunter, Savin and Dahl. Clinical Dermatology 3rd Edition. Massachusetts: Blackwell Science LTD; 2002
- The Merck Manual of Medical information. Merck Research Laboratories; 1997
