What is Anatomical snuff box?
It is a triangle-shaped depression on the lateral part of the dorsum of the hand. What is the medical term for snuff box? In the medical field, it is called radial fossa. In the medical term, a fossa pertains to a hollow depression/semi-flattened surface.
The snuff box is located at the level of the carpal bones. If you try to locate the snuff box, all you have to do is to extend your thumb. It is fondly called the snuff box because it was used to hold snuff (ground tobacco) as it inhaled through the nose. (1, 2, 3)
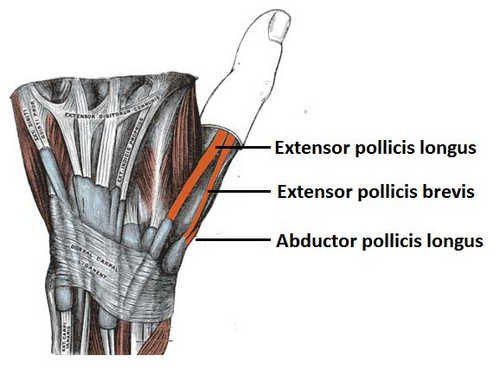
Image 1: The borders of the anatomical snuff box.
Picture Source: cdn1.teachmeseries.com
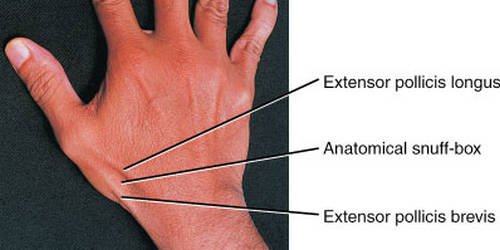
Picture 2: The image showing how to properly and accurately locate the anatomical snuff box.
Photo Source: medicine.academic.ru
Anatomical snuff box borders
- Ulnar – It is the medial border specifically the extensor pollicis longus tendon.
- Radial – it is the lateral border, which includes the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis tendons.
- Proximal – It includes the radius’ styloid process. (2, 3, 4)
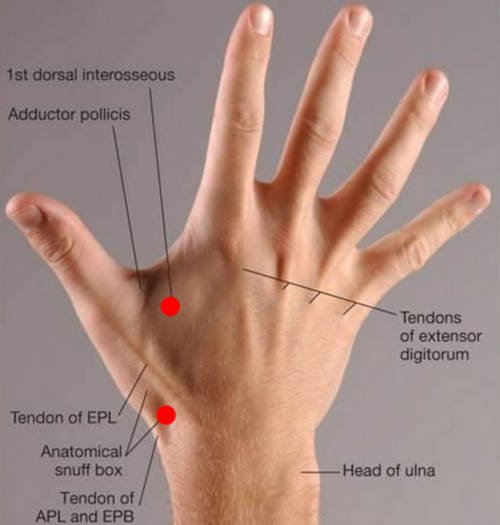
Photo 3: The anatomical snuff box along with other important structures.
Image Source: pbs.twimg.com
What are the contents of the anatomical snuff box?
The primary contents of the anatomical snuff box are:
Radial artery
It crosses the anatomical snuff box’s floor in an oblique way leading to the extensor tendons. If you place your two fingers near the anatomical snuff box, you can easily palpate the radial pulse.
Branches of radial nerve
The terminal branches of the radial nerve run across the upper parts of the anatomical snuff box.
Cephalic vein
It crosses the anatomical snuff box. (4, 5, 6)
The anatomical snuff box location
The anatomical snuff box is strategically located on the thumb side of the hand or in the medical term the lateral/radial part of the hand. To locate your snuff box, you have to do the following:
- Spread all the five fingers out/make your hands look wide.
- Notice a small indentation on the wrist; that is your anatomical snuff box.
- Try to give someone a thumbs up and the snuff box will be visible at the wrist joint. (2, 4, 5, 6)
Anatomical snuff box from a skeletal standpoint
From a skeletal standpoint, the snuff box is located over the carpals; the group of bones found in the wrist. There are eight uniquely shaped bones in the wrist.
The carpal bone, specifically the scaphoid bone serves as the floor of the anatomical snuff box. It is the foundation of the anatomical snuff box. (6, 7, 8)
The anatomical snuff box from a muscular standpoint
The anatomical snuff box has two thin and chord-like structures forming the snuff box’s triangular shape creating the divot.
The medial border has the tendon of the extensor pollicis longus muscle. The lateral border of the snuff box has the tendons of the muscles pollicis longus (abductor) and pollicis brevis (extensor). (7, 8)
Nerves and blood supply
The anatomical snuff box has nerves and arteries supplying the area with blood and making it responsible for various sensation.
- Radial artery – It supplies blood to the essential parts of the wrist and hand.
- Radial nerve – It provides sensation and functions. (6, 7, 8)
Anatomical snuff box clinical significance
Scaphoid fracture
The scaphoid together with the radius articulate forming the wrist joint. If a person sustains a fall on an outstretched hand, it could cause a severe blow to the wrist leading to excruciating pain. A localized pain in the anatomical snuff box is most likely due to scaphoid fracture.
It is something that should not be taken lightly because any forms of fracture to the scaphoid could greatly affect the blood supply to the proximal part of the anatomical snuff box. Failure to address the problem right away could lead to avascular necrosis and arthritis.
Idiopathic radial artery aneurysm of the anatomical snuff box
It is an extremely rare condition and is linked to trauma that is penetrating in nature. (8, 9, 10)

Image 4: The anatomical snuff box/scaphoid fracture as manifested by wrist pain.
Picture Source: acuclinic.com.au
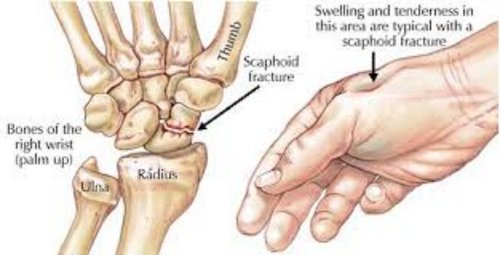
Picture 5: Swelling and tenderness are the cardinal signs of anatomical snuff box fracture.
Photo Source: encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com
Anatomical snuff box injury
If you are suspecting an anatomical snuff box injury, a thorough physical examination and diagnostic procedure should be performed.
Physical examination
- Compare the injured wrist with an uninjured wrist.
- Check for signs of tenderness on examination as it is one of the cardinal signs of scaphoid fracture.
- Check for the tenderness of the scaphoid tubercle. The doctor extends the wrist of the patient with one hand and applies pressure to the tuberosity using the opposite hand. If no tenderness is felt, then the patient does not have a scaphoid fracture.
- Pain with an anatomical snuff box compression test. The patient’s thumb is compressed along the line of the first metacarpal.
- Pain in the snuff box as the wrist is pronated secondary to the ulnar deviation. (1, 6, 9, 10)
Imaging studies
Plain radiographs
To evaluate a fracture in the anatomical snuff box, a radiographic view; anteroposterior, lateral, and oblique should be done.
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
It is ordered to detect anatomical snuff box fracture the earliest possible time because MRI is specific and sensitive.
Ultrasonography
A high spatial resolution ultrasonography is performed to identify occult scaphoid fracture.
Bone scintigraphy
It is done to detect occult fracture of the anatomical snuff box and other bones. It is more accurate and cost-effective compared to other imaging studies. (2, 4, 6, 7)
Anatomical snuff box fracture Treatment
The type of treatment for anatomical snuff box fracture depends on the extent and severity of the fracture. For someone with a suspected anatomical snuff box fracture and negative radiograph, the best approach is to apply a short arm thumb spica and the fracture needs to be evaluated in 10 to 14 days.
It is important to apply a cast the right way as failure to do so can worsen the patient’s condition. A bone scintigraphy might be needed should the patient opted for an alternative treatment method. (2, 5, 9)
References:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anatomical_snuffbox
- http://teachmeanatomy.info/upper-limb/areas/anatomical-snuffbox/
- https://radiopaedia.org/articles/anatomical-snuff-box
- https://www.physio-pedia.com/Anatomical_snuff_box
- https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-is-the-anatomical-snuffbox-muscles-anatomy.html
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482228/
- https://www.medicinenet.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=13291
- http://sketchymedicine.com/2011/12/the-anatomical-snuff-box-and-dequevains-tenosynovitis/
- https://www.howtorelief.com/anatomical-snuffbox/
- http://masterofmedicine.com/anatomical-snuffboxboundaries-and-contents/






