What is Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever
Ebola virus disease (EVD) or Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF) is a severe fatal disease that can affect both humans and primates. Four viruses which causes the disease in humans are the Bundibugyo virus (BDBV), Sudan Virus (SUDV), Ebola Virus (EBOV) and Taj Forest Virus (TAFV), which is also known as the Côte d’Ivoire Ebola Virus (CIEBOV).
The disease got its name from the Ebola River in the Democratic Republic of Congo (formerly known as Zaire) in Africa where it was first recognized. The fifth virus, the Ebola-Reston, caused the disease among primates.This virus has recently been found in the Philippines.
Ebola hemorrhagic fever first broke out in Sudan and Zaire in 1976 causing one of the highest fatality rates at 90%.
How is the Ebola Virus Transmitted?
The Ebola virus belongs to the family Filoviridae. The disease can be transmitted to humans from infected animals as well as through direct contact by a human to infected body fluids or needles.
Nosocomial transmission during Ebola outbreak can also be possible. Although airborne transmissions have been documented among monkeys, there is still no known evidence of such transmission occurring among humans.
Signs and Symptoms
The signs are symptoms of quite similar to that of Marburg Virus Disease (MVD), which is also another type of viral hemorrhagic fever. The incubation period for the virus would usually take place between 2 to 25 days.
- Fever, headache, muscle and joint pains, sore threat, and weakness are usually the first signs of Ebola hemorrhagic fever. These influenza-like symptoms may also accompanied by diarrhea and vomiting as well as stomach aches.
- Sore throat, cough, dyspnea, hiccups and pharyngitis may also manifest as part of the illness.
- Hemorrhage is a late symptom of the disease. This could include bleeding from the eyes, ears and nose. In addition, eye swelling could also occur.Some people even experience genital swelling in their labia or scrotal area. Hemorrhage usually occurs as the virus tends to affect the ability of the blood to coagulate thereby causing bleeding in various parts of the body. Maculopapular rashes can also appear and be a form of bleeding in the skin. Hematemesis (vomiting of blood), hemoptysis (coughing up of blood) and melena (black, tarry stools) are also manifestations of possible bleeding with Ebola hemorrhagic fever.
The development of hemorrhage can be indicative of a poor prognosis as it can eventually lead to multiple organ dysfunction syndromes, focal tissue necrosis or disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Ebola Virus Pictures
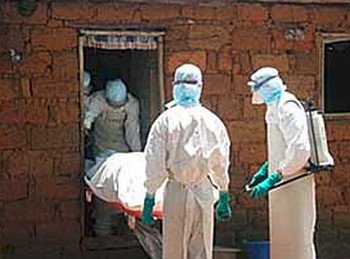
Medical Experts Handling blood from a patients with this condition is an extreme bio-hazard
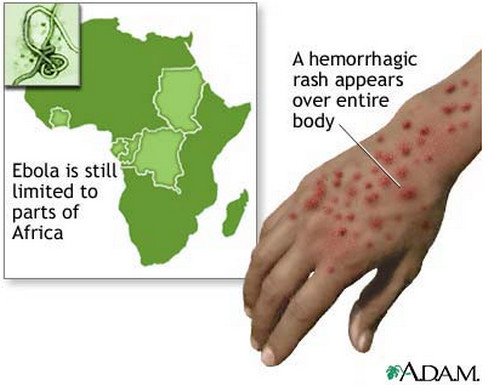
Picture 2 : Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever rash on hand
Image source : ADAM
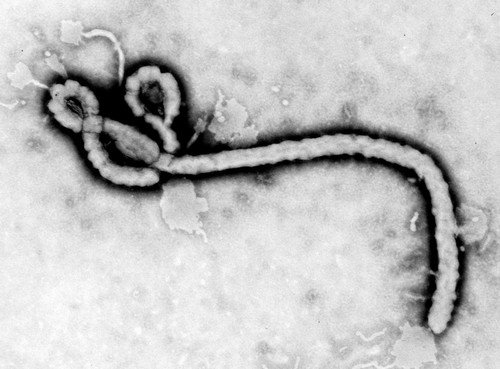
Picture : Ebola Virus
Diagnosis of Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever
As Ebola hemorrhagic fever manifests similar signs and symptoms to other viral hemorrhagic diseases, it may be difficult to diagnose at the initial onset of the disease. Signs like red eyes and skin rashes could be indicative of various viral diseases. However, with proper physical assessment as well as interrogation of possible exposures to an Ebola virus, a definitive diagnosis may be made.
Taking a look into a person’s medical history would be an important tool in diagnosing the illness as the medical history would reveal a travel or exposure to wildlife. Confirmatory diagnosis for the Ebola hemorrhagic fever can be done through the isolation of the virus or through identification of the Ebola virus antigen or genomic or subgenomic RNAs in an infected person’s blood samples during the acute phase. Meanwhile, IgM and IgG antibodies could be tested during the later phase of the disease.
Treatment for Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever
Unfortunately, there is no specific treatment for Ebola hemorrhagic fever. Patients suffering from this disease would usually have supportive therapy. This would include minimizing invasive procedures, balancing fluids and electrolytes, anticoagulant therapy to prevent the occurrence of bleeding, oxygen maintenance, management of pain as well as the administration of antibiotics to address secondary infections.
A patient diagnosed with Ebola hemorrhagic fever would usually require an admission to the intensive care unit for better monitoring. Blood or platelet transfusion may also be necessary to correct coagulation problems and blood loss.
Ways to Prevent Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever
Prevention of Ebola hemorrhagic fever can prove a challenge as it is highly contagious and infectious. Personal protective equipment is necessary especially for those who are greatly exposed to the Ebola virus like medical practitioners and laboratory technicians.
Ebola hemorrhagic fever is a fatal condition that requires the immediate attention of a physician. Although no definitive treatments are available at this point, the worsening of the condition can be avoided and prevented as long as prompt medical treatment is given to a patient suffering from this condition.
References:
http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/dvrd/spb/mnpages/dispages/Fact_Sheets/Ebola_Fact_Booklet.pdf
